Many disease-related processes happen by way of protein complexes which are thought of undruggable with small molecules.
An instance is RAS, which is regularly mutated in most cancers and contributes to initiation and upkeep of the illness by constitutive sign transduction via protein interplay with effector proteins, like PI3K, RAF and RALGDS. Such protein interactions are due to this fact important targets for remedy.
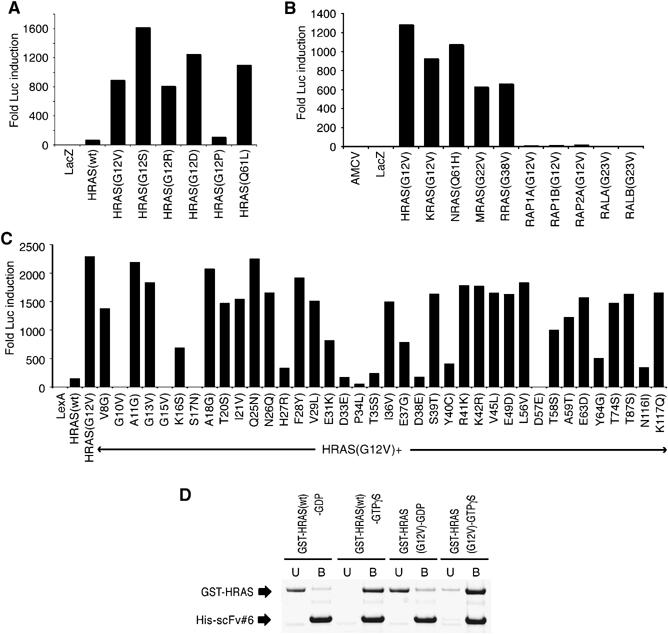
We describe a single immunoglobulin variable area area that particularly binds to activated GTP-bound RAS and prevents RAS-dependent tumorigenesis in a mouse mannequin.
The crystal construction of the immunoglobulin-RAS complicated reveals that the variable area competitively binds to the conformationally variant areas of RAS, the place its signalling effector molecules work together.
This enables the plasma membrane focused single area intrabody to inhibit signalling by mutant RAS. This mode of motion is a novel advance to immediately intervene with oncogenic RAS perform in human most cancers and reveals a universally relevant strategy to develop macromolecules to fight most cancers.
As well as, this technique illustrates a normal means for interfering with protein interactions which are generally thought of intractable as typical drug targets.
Tumour prevention by a single antibody area concentrating on the interplay of sign transduction proteins with RAS.
A therapeutic anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody inhibits T cell receptor sign transduction in mouse autoimmune cardiomyopathy.
BACKGROUNDT cell immune abnormalities in sufferers with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) has been intensively studied over the previous 10 years.
Our earlier examine has prompt that immunization of mice with the peptides derived from human adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT) outcome within the manufacturing of autoantibodies in opposition to the ANT and histopathological adjustments much like these in human DCM.
The ANT peptides can induce autoimmune cardiomyopathy like DCM in Balb/c mice. On this examine we aimed to concentrate on the molecular mechanism of T cells within the autoimmune cardiomyopathy mouse mannequin by detecting the expression of the 2 T cell signaling molecules.
METHODSThe ANT peptides had been used to trigger autoimmune cardiomyopathy in Balb/c mice. Anti-L3T4 or rat anti-mouse IgG was administered to the mice (n = 6 in every group) concurrently immunized with ANT. ELISA evaluation was used to detect autoantibodies in opposition to the ANT peptides and the odds of interferon-gamma and interleukin-Four producing cells amongst splenic CD4(+) lymphocytes was decided by utilizing circulation cytometry evaluation.
The expression of CD45 in spleen T cells was decided by immunohistochemistry and the mRNAs of T cell signaling molecules had been detected by real-time PCR.
RESULTSTreatment of ANT immunized Balb/c mice with anti-CD4 mAb brought about a discount within the gene expression of P56lck and Zap-70 and a decrease degree of CD45 expression by spleen T cells.
Additionally, a reverse of the Th1/Th2 ratio that ends in the diminished manufacturing of antibodies in opposition to ANT was discovered within the anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) group. Whereas irrelevant antibody (rat anti-mouse IgG) didn’t suppress T cell signaling molecules nor inhibit CD45 expression, and control-antibody mice didn’t present any important variations in contrast with the DCM group.
CONCLUSIONSThe outcomes present that anti-CD4 mAb is a strong inhibitor of the early initiating occasions of T cell receptor (TCR) sign transduction in mouse autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy.
